Establishing Reliability and Validity of a High Leverage Practice Rubric for Assessment (HLPR-A)
Abstract
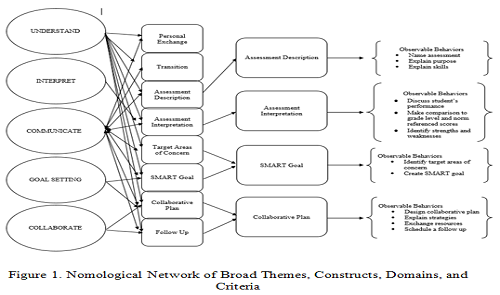
The purpose of the current research study was to establish reliability and validity of an assessment high-leverage practice rubric (HLPR-A). Five raters scored 33 participants’ instructional videos two times using the HLPR-A. Interrater and intrarater reliability was established using an intraclass correlation coefficient. Content validity was established through expert review. Construct validity was presented using a nomological network. Internal validity was confirmed using principal axis factor analysis. The results revealed the HLPR-A to be a reliable and valid tool for assessing preservice teachers’ performance when interpreting and communicating assessment information to a parent during a parent-teacher conference using mixed reality virtual simulations. Future research could explore using the HLPR-A on other populations, with a variety of raters, in other environments, and programs.
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Alghadir, A., Anwer, S., & Brismee, J. M. (2015). The reliability and minimal detectable change of timed up and go test in individuals with grade 1–3 knee osteoarthritis. BioMed Central Musculoskeletal Disorders, 16(1), 174-174. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-015-0637-8
Beachcroft-Shaw, J. & Ellis, D. (2020). Finding common ground: Mapping the nomological networks of sustainability constructs for improved social marketing. Sustainability Science, 15, 745-758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-019-00755-z
Council for Exceptional Children. (2020). Initial Practice Based Professional Standards for Special Education. https://exceptionalchildren.org/standards/initial-practice-based-professional-preparation-standards-special-educators
Cronbach, L. J. & Meehl, P. E. (1955). Construct validity in psychological tests. Psychological Bulletin, 52, 281-302.
Field, A. (2018). Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics (5th ed). Sage.
Firmansyah, Dr. R., Nahadi, N, & Firman, H. (2020). Development of performance assessment instruments to measure students’ scientific thinking skill in the quantitative analysis acetic acid levels. Journal of Educational Science, 4(3), 459-468 https://doi.org/10.31258/jes.4.3
Gallardo, K. (2020). Competency-based assessment and the use of performance-based evaluation rubrics in higher education: Challenges towards the next decade. Problems of Education in the 21st Century, 78(1), 61-79. https://doi.org/10.33225/pec/20.78.61
Johnson, R. L. & Morgan, G. B. (2016). Survey Scales: A guide to development, analysis, and reporting. Guildford Press.
Johnson, E. S., Zheng, Y., Crawford, A. R., & Moylan, L. A. (2019). Developing an explicit instruction special education teacher observation rubric. The Journal of Special Education, 53(1), 28-40. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022466918796224
Jones, B. A., & Peterson-Ahmad, M. B. (2017). Preparing new special education teachers to facilitate collaboration in the individualized education program process through mini conferencing. International Journal of Special Education, 32(4), 697-707. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1184062.pdf
Jonsson, A. (2014). Rubrics as a way of providing transparency in assessment. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education, 39(7), 840-852. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2013.875117
Jonsson, A., & Svingby, G. (2007). The use of scoring rubrics: Reliability, validity, and educational consequences. Educational Research Review, 2, 130-144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2007.05.002
Kaiser, H. F. (1960). The application of electronic computer to factor analysis. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 20(1), 141-151. https://doi.org/10.1177/001316446002000116
Koo, T. K., & Li, M. Y. (2016). A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine, 15, 155-163. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcm.2016.02.012
McLeskey, J., Barringer, M-D., Billingsley, B., Brownell, M., Jackson, D., Kennedy, M., Lewis, T., Maheady, L., Rodriguez, J., Scheeler, M. C., Winn, J., & Ziegler, D. (2017). High-leverage practices in special education. Arlington, VA: Council for Exceptional Children & CEEDAR Center. https://ceedar.education.ufl.edu/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/CEC-HLP-Web.pdf
Reddy, Y. M. & Andrade, H. (2010). A review of rubric use in higher education. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 35(4), 435-448. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602930902862859
Van Helvoort, J., Brand-Gruwel, S., Hyusmans, F., & Sjoer, E. (2017). Reliability and validity test of a scoring rubric for information literacy. Journal of Documentation, 73(2), 305-316. https://doi.org/10.1108/JD-05-2016-006
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.31258/jes.6.4.p.707-722
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2022 Deana J. Ford, Sara E. Luke, S. Michelle Vaughn

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Publisher: FKIP Universitas Riau













