Cross-Age Peer-Tutoring: An Effective Strategy for Enhancing Students’ Retention in Mathematics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31258/jes.9.1.p.208-230Keywords:
coordinate-Geometrycoordinate-Geometry, cross-age, peer-tutoring, retention-spanAbstract
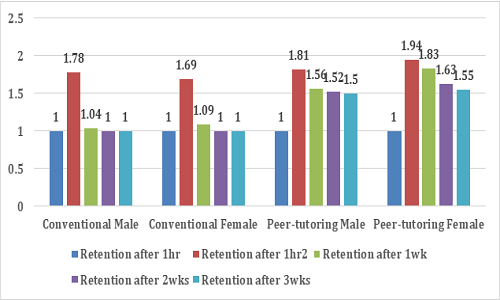
The alarming rate of students’ underachievement in mathematics as linked to short retention is calling for urgent involvement of stakeholders. In view of this, this study investigated the effects of cross-age peer-tutoring as an intervention on students’ retention in mathematics. By means of multi-stage sampling technique, a total of 93 senior secondary school 2 (Grade-11) students (59-control & 34-Experimental groups) were sampled in their intact classes. The study adopted the quasi-experimental research design using the pre-test-post-test non-equivalent control group experimental approach. Three research questions and three null hypotheses guided the study, which lasted for five weeks. The self-developed students’ achievement test in coordinate geometry (SATC) has Pearson-R coefficient of 0.74, while mean, standard deviation and Analysis of Covariance were used as statistical tools. The study found significant effect of cross-age peer-tutoring strategy on retention of students in mathematics [F(3, 134)=8.15; p<0.05] revealed no statistical significant influence of gender on students’ retention [F(1, 134)= 1.24; p>0.05 and no statistical significant influence of age on students’ retention [F(2, 134)= 0.33; p>0.05]. It concluded that cross-age peer-tutoring is an effective strategy for extending students’ retention in mathematics, irrespective of gender and age. It is neither gender bias nor age sensitive. To boost learning outcome in mathematics teachers should generously teach difficult concept like coordinate geometry using a peer-tutoring strategy.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Kennedy O. Akudo, Adetunji, A. Olaoye, Olawale Sojinu, Ibraheem A. Alabi, Iyore Evelyn Chukwulobe, Olasunkanmi, A. Gbeleyi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.